If search engines can’t properly crawl and index your website, even the best content in the world won’t rank.
Many websites struggle not because of poor content or weak links, but due to hidden crawlability issues that silently block search engine bots. These crawlability problems limit visibility, waste crawl budget, and prevent pages from appearing in search results.
In this in-depth guide, you’ll learn:
- what crawlability and indexability really mean
- common crawlability problems websites face
- how to fix crawl accessibility issues step by step
- 13 practical actions to improve how search engines discover and understand your site
This is a complete, actionable roadmap you can follow in 2026 and beyond.
What Is Crawlability And Indexability?
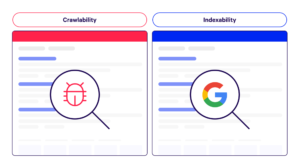
Before diving into fixes, let’s clarify the basics.
Crawlability refers to how easily search engine bots can access and navigate your website.
Indexability refers to whether those crawled pages are allowed to be stored and shown in search results.
A page can be:
- crawlable but not indexable
- indexable but rarely crawled
- neither crawlable nor indexable
Strong SEO requires both.
Most crawlability issues stem from poor technical setup, slow performance, or confusing site structure—not from content quality.
Steps To Boost Your Site’s Crawlability And Indexability
1. Improve Page Loading Speed
Speed is one of the most overlooked crawl accessibility factors.
Search engines allocate limited time to crawl each website. If pages load slowly, fewer URLs get crawled, leading to crawlability problems.
Why Speed Matters for Crawlability
- slow pages waste crawl budget
- bots abandon delayed responses
- large sites suffer the most from speed-related crawlability issues
How to Improve Loading Speed
- compress images
- use caching
- minimize JavaScript and CSS
- reduce server response time
Faster pages = better crawl accessibility + improved user experience.
2. Measure & Optimize Core Web Vitals
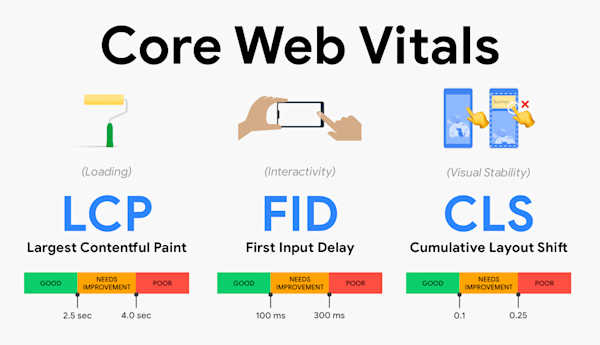
Core Web Vitals are user-focused metrics, but they indirectly affect crawlability.
Poor performance signals often correlate with:
- heavy scripts
- unstable layouts
- slow rendering
These factors contribute to crawlability problems by making pages harder to process efficiently.
Key Metrics to Optimize
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Improving these metrics creates cleaner, faster pages that are easier for bots to crawl and index.
3. Optimize Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is the number of pages search engines are willing to crawl on your site within a given time.
Common Crawlability Issues Related to Crawl Budget
- too many low-value pages
- parameter-based URLs
- faceted navigation creating infinite URLs
- duplicate or near-duplicate content
How to Optimize Crawl Budget
- block unnecessary URLs via robots.txt
- consolidate duplicate pages
- remove thin or outdated content
- improve internal linking to priority pages
Efficient crawl budget usage reduces crawlability problems and improves index coverage.
4. Strengthen Internal Link Structure
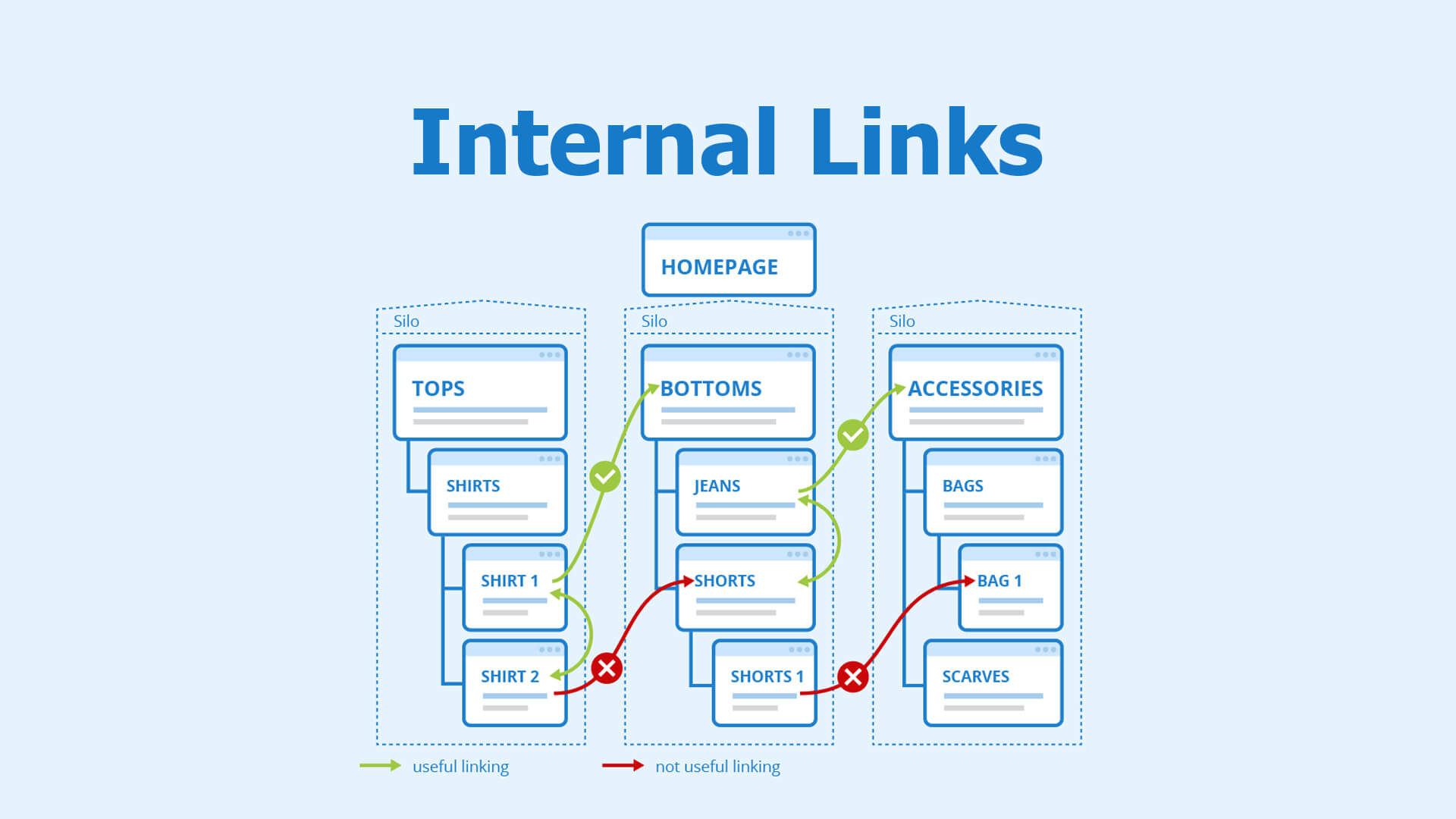
Internal links are the primary pathways search engines use to discover content.
Weak internal linking creates crawl accessibility gaps where important pages remain hidden.
Internal Linking Best Practices
- use clear, descriptive anchor text
- link from high-authority pages to important pages
- avoid orphan pages (pages with no internal links)
- maintain a logical site hierarchy
Strong internal linking solves many crawlability issues without touching technical code.
5. Submit Your Sitemap To Google
An XML sitemap acts as a roadmap for search engines.
While not a replacement for good internal linking, it helps bots discover URLs faster—especially on large or frequently updated sites.
Sitemap Best Practices
- include only canonical, indexable URLs
- remove redirected or blocked pages
- update automatically when new content is published
A clean sitemap improves crawl accessibility and reduces indexing delays.
6. Update Robots.txt Files
Robots.txt controls what search engines can and cannot crawl.
Incorrect rules are a major source of crawlability problems.
Common Robots.txt Crawlability Issues
- blocking important directories
- blocking CSS or JavaScript files
- outdated rules after site migrations
Best Practices
- review robots.txt after every major site change
- block only low-value or private sections
- never block important content unintentionally
One wrong line can create massive crawl accessibility issues.
7. Check Your Canonicalization
Canonical tags help search engines understand which version of a page is the primary one.
Incorrect canonicalization causes:
- duplicate content confusion
- wasted crawl budget
- indexing of the wrong URLs
Canonical Best Practices
- self-reference canonical URLs
- avoid conflicting signals (canonical + noindex)
- ensure canonicals point to indexable pages
Proper canonicalization resolves many hidden crawlability problems.
8. Perform A Site Audit
Regular site audits uncover technical and structural crawlability issues before they cause damage.
What a Crawlability-Focused Audit Should Check
- crawl errors
- index coverage issues
- blocked resources
- redirect chains
- duplicate pages
Audits transform assumptions into actionable insights.
Check Your Indexability Rate
Indexability rate = indexed pages ÷ indexable pages.
A low rate signals serious crawlability problems.
Common Causes
- noindex tags
- canonical conflicts
- poor content quality
- crawl accessibility limitations
Monitoring this metric helps diagnose issues early.
Audit (And Request Indexing) Newly Published Pages
New content doesn’t always get indexed automatically.
Best Practices
- ensure new pages are internally linked
- include them in your sitemap
- request indexing for priority pages
This speeds up discovery and prevents crawl delays.
9. Check For Duplicate Content
Duplicate content creates confusion and wastes crawl budget.
Common Duplicate Content Sources
- URL parameters
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- trailing slashes
- printer-friendly pages
How to Fix Duplicate Content
- consolidate URLs
- use canonical tags
- apply redirects where appropriate
Reducing duplication eliminates major crawlability problems.
10. Eliminate Redirect Chains And Internal Redirects
Redirect chains force bots to hop through multiple URLs before reaching content.
Why Redirect Chains Hurt Crawlability
- waste crawl budget
- slow down discovery
- increase error risk
Best Practices
- update internal links to final URLs
- reduce redirects to a single hop
- remove outdated redirects
Cleaner paths mean better crawl accessibility.
11. Fix Broken Links
Broken links lead bots to dead ends.
Crawlability Problems Caused by Broken Links
- wasted crawl budget
- incomplete crawling
- poor site quality signals
Fix Strategy
- regularly scan for broken links
- replace or remove invalid URLs
- ensure internal links always point to live pages
Healthy links keep crawlers moving efficiently.
12. Use IndexNow (Where Supported)
IndexNow allows websites to notify search engines instantly when content changes.
Benefits of IndexNow
- faster indexing
- reduced crawl delays
- improved crawl efficiency
For large or frequently updated sites, IndexNow significantly improves crawl accessibility.
13. Implement Structured Data To Enhance Content Understanding
Structured data helps search engines understand page context—not just crawl it.
Why Structured Data Helps Crawlability
- clarifies page purpose
- reduces misinterpretation
- supports rich results
While it doesn’t directly increase crawling, it improves how crawled pages are processed and indexed.
FAQs
What is crawlability in SEO?
Crawlability refers to how easily search engine bots can access, navigate, and discover pages on your website.
What causes crawlability problems?
Common causes include slow page speed, poor internal linking, blocked resources, duplicate content, and redirect chains.
What is crawl accessibility?
Crawl accessibility means ensuring bots can reach important pages without technical or structural barriers.
How do I find crawlability issues?
Use site audits, crawl reports, index coverage data, and log file analysis to identify crawlability problems.
Does crawlability affect rankings?
Indirectly, yes. Pages that aren’t crawled or indexed cannot rank, regardless of content quality.
Conclusion
SEO doesn’t start with keywords or links—it starts with crawlability.
By addressing crawlability problems, improving crawl accessibility, and following these 13 steps consistently, you ensure your content has a real chance to be discovered, indexed, and ranked.
A digital marketer with a strong focus on SEO, content creation, and AI tools. Creates helpful, easy-to-understand content that connects with readers and ranks well on search engines. Loves using smart tools to save time, improve content quality, and grow online reach.

