In the digital age, visibility is everything. Whether you’re running a small local business, a large online store, or a personal blog, people need to find you online. That’s where SEO marketing plays a powerful role. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what SEO is, why it’s essential, how it works, and how you can use it to grow your online presence and business success.
What Is SEO Marketing?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) marketing is a technique used to make your website appear higher in search engine results like Google or Bing. The higher your site ranks, the more people will visit it.
Think of SEO like this: Imagine you have a shop in a busy market. SEO is like putting up bright signs, using clear directions, and having the best-looking storefront—so people notice you first instead of your competitors.

The Role of SEO in the Digital Marketing Ecosystem
SEO is not a standalone strategy. It works best when combined with other digital marketing methods such as:
- Content Marketing: Writing blogs, articles, or guides that answer people’s questions.
- Social Media Marketing: Sharing your content and engaging with your audience on platforms like Instagram or LinkedIn.
- Email Marketing: Sending newsletters to keep users updated and engaged.
While paid ads bring short-term traffic, SEO is the long-term game that brings consistent results even after your campaign ends.
Who Needs SEO Marketing?
The simple answer is—everyone with a website. Here’s who benefits the most:
- Small businesses wanting to reach local customers.
- eCommerce stores trying to increase product visibility.
- Bloggers aiming to build an audience.
- Startups wanting to grow brand awareness.
- Enterprises improving their long-term digital footprint.
Why Is SEO Important for Businesses Today?
Organic Traffic and Credibility
When your website ranks high on Google, people trust it more. Research shows that the top 3 results on Google get more than 50% of all clicks. SEO helps you get into those top spots—without paying for every visitor.
For example, if someone searches “best yoga mat for beginners,” and your blog appears on the first page with helpful advice, they’re more likely to trust and buy from you.
Long-Term ROI Compared to Paid Ads
Paid ads work like renting space—you pay for traffic. Once the budget is gone, so is the traffic. But SEO is like owning property. You invest in content and website improvements, and over time, they continue bringing visitors without additional cost.
Businesses often see high returns from SEO because they get traffic continuously without paying per click.
SEO’s Impact on Brand Awareness
Even if users don’t click on your site right away, seeing your name on the first page helps with brand recall. Over time, this builds recognition, authority, and loyalty.
How Search Engines Work
Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained
Search engines use bots, also called “spiders” or “crawlers,” to browse the web. They do three main things:
- Crawling: Bots visit your web pages and follow links.
- Indexing: They save your content in a giant database.
- Ranking: When someone searches, the engine shows results in order of relevance and usefulness.
For example, if you write a blog on “how to start gardening,” Google crawls and indexes your content. If it’s helpful and well-optimized, it might show up when someone searches for that topic.
How Algorithms Determine Page Rankings
Google’s algorithm looks at hundreds of ranking factors, including:
- Content quality
- Keyword usage
- Website speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- Backlinks from other websites
It then decides which pages are most helpful for the searcher’s query.
SEO vs. SEM: Understanding the Difference
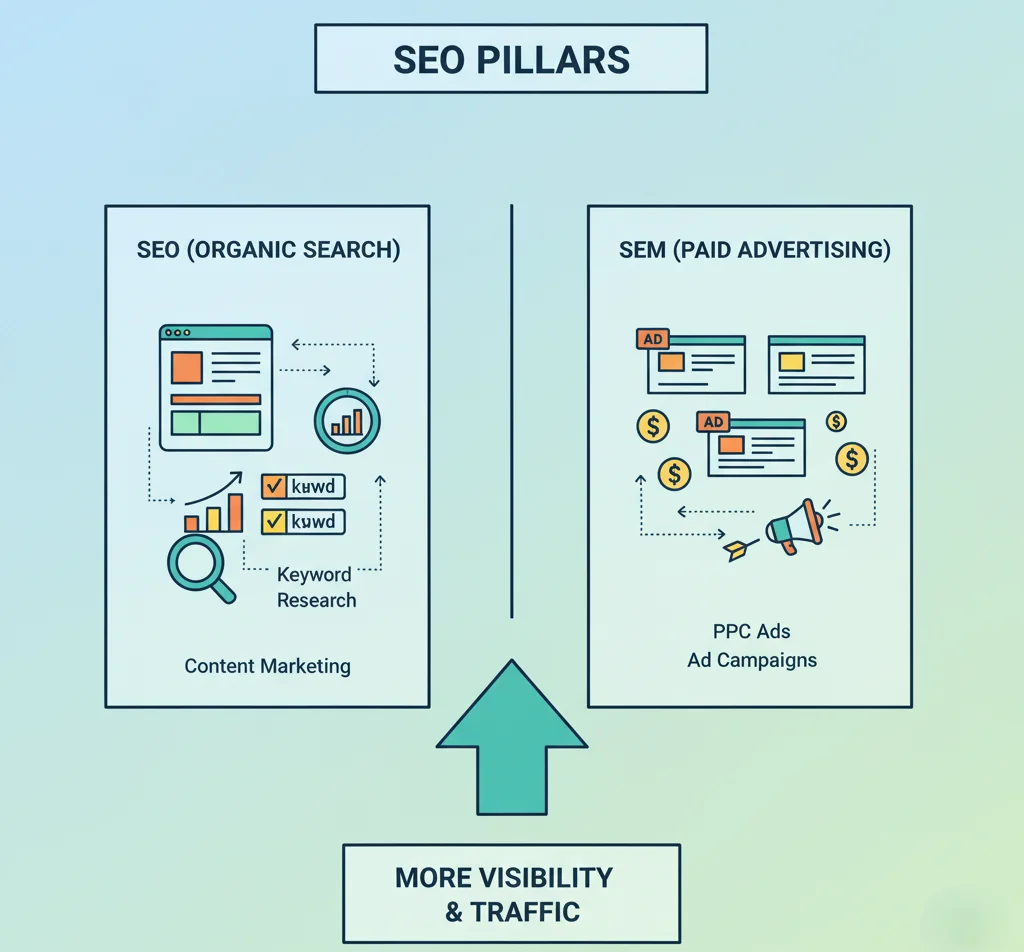
What is SEM (Search Engine Marketing)?
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a broad strategy that includes both:
- SEO: Getting traffic organically.
- PPC (Pay-per-click): Paying for traffic through ads (e.g., Google Ads).
Key Differences Between SEO and PPC
| Feature | SEO | PPC |
| Cost | Free traffic (but time/cost to optimize) | Paid traffic per click |
| Time to See Results | Slower (3-6 months) | Immediate |
| Long-term Impact | Lasting benefits | Stops when ads stop |
| Trust Factor | Higher (organic = credibility) | Lower (ads marked as “sponsored”) |
When to Use SEO, PPC, or Both
- Use SEO for long-term growth and brand visibility.
- Use PPC for quick campaigns like a product launch or holiday sale.
- Use both to dominate both organic and paid results.
Also Check: 11 Lead Generation Strategies & Tactics That Work
The Core Pillars of SEO
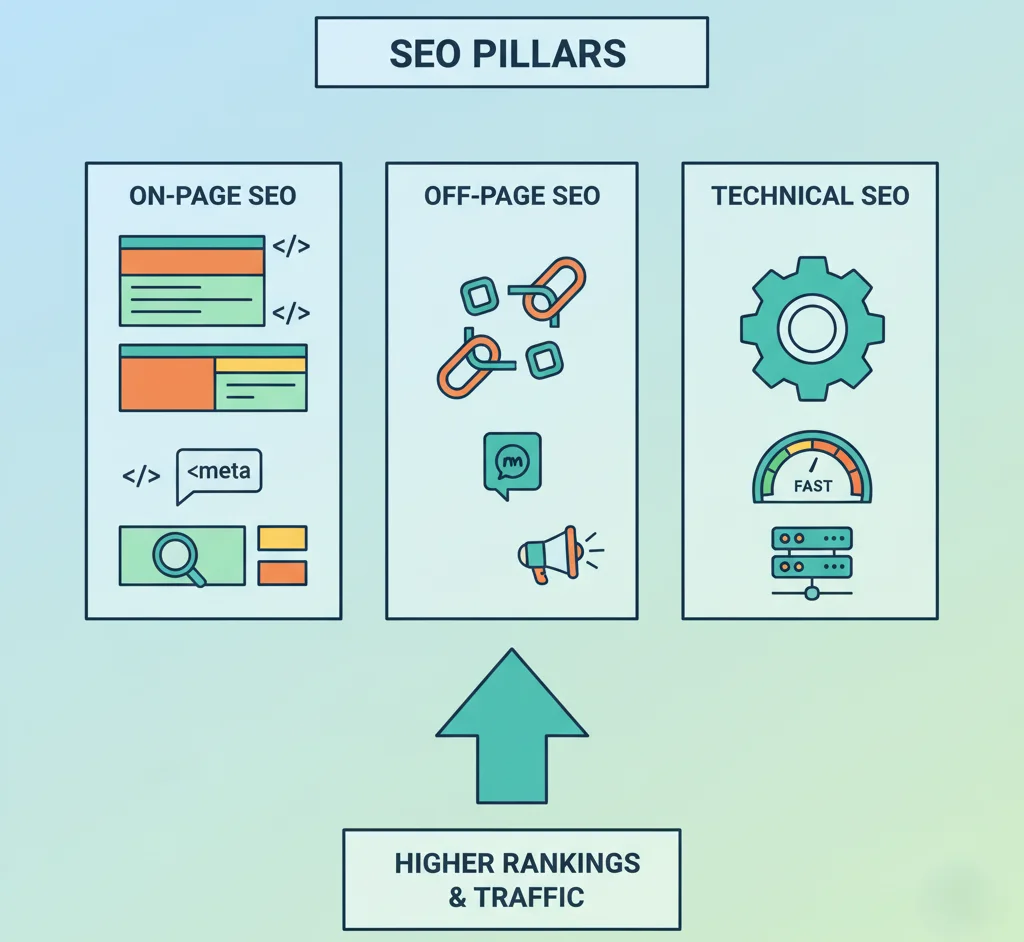
On-Page SEO
Content Optimization (Search Intent, Readability, E-E-A-T)
Good SEO content solves real problems. Your articles, product pages, or guides should:
- Match search intent (what the user is looking for).
- Be easy to read (short paragraphs, bullet points).
- Follow Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines:
- Experience: First-hand knowledge
- Expertise: Knowledgeable and trustworthy
- Authoritativeness: Cited by others
- Trustworthiness: Safe and transparent
HTML Elements
Your website’s HTML elements should include:
- Title Tag: The clickable headline in search results.
- Meta Description: A short summary that invites clicks.
- URL Structure: Clean and keyword-friendly URLs.
- Alt Text: Descriptions for images (important for accessibility and image SEO).
- Headings: Use H1 for the main title, H2/H3 for subtopics.
Website Structure & Internal Linking
Organize your website so users can easily find information. Use internal links to connect related content, which helps both users and search engines.
Off-Page SEO
Backlinks and Authority
A backlink is when another website links to yours. Google sees this as a vote of confidence. More high-quality backlinks = higher trust = better rankings.
Social Proof and Mentions
If people are talking about your brand on social media, forums, or news websites, it sends positive signals to search engines.
Local SEO & Citations

For local businesses:
- Claim your Google Business Profile.
- Get listed on local directories (Yelp, Justdial, etc.).
- Encourage customer reviews.
Technical SEO
Website Speed & Core Web Vitals
Fast websites provide a better user experience. Google’s Core Web Vitals measure how fast your page loads, how interactive it is, and how visually stable it remains.
Mobile-Friendliness
More than half of searches happen on mobile. Use responsive design so your site looks good on all devices.
Secure Connections (HTTPS)
Make sure your website uses HTTPS. It’s safer and preferred by Google.
Crawlability & Indexation
Use tools like Google Search Console to submit your sitemap and check for crawling errors.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
This is code you add to your website that helps search engines understand your content better. For example, adding recipe schema to a cooking blog helps Google show ratings, ingredients, and cooking time.
Must-Know SEO Techniques and Strategies
- Keyword Research: Use tools like Ubersuggest or Ahrefs to find what your audience searches for.
- Content Creation: Write long-form, helpful content that answers user questions.
- User Engagement: Keep people on your site longer with great UX and internal links.
- Analytics: Measure what works and what doesn’t. Keep optimizing.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Using too many keywords in one page (keyword stuffing)
- Publishing thin content (less than 300 words with little value)
- Ignoring meta descriptions or title tags
- Not optimizing for mobile
- Forgetting to update outdated content
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Started with SEO

Step 1: Understand How Search Works
Learn how Google ranks websites.
Step 2: Do Effective Keyword Research
Focus on long-tail keywords (e.g., “best running shoes for flat feet”).
Step 3: Optimize On-Page Content
Use keywords naturally. Add internal links and improve readability.
Step 4: Build Authority with Off-Page SEO
Reach out for backlinks. Share your content on social platforms.
Step 5: Fix Technical Issues
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Site Audit tools to find issues.
Step 6: Measure and Improve
Check your rankings, traffic, bounce rate, and page speed regularly.
How to Measure & Track SEO Success
Key SEO Metrics
- Organic traffic (via Google Analytics)
- Keyword rankings (via Ahrefs, SEMrush)
- Conversion rate (how many visitors take action)
- Bounce rate (if people leave quickly, something’s wrong)
Tools for Tracking SEO
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Ahrefs / SEMrush / Ubersuggest
How to Interpret SEO Reports
Look for:
- Increases in traffic
- More ranking keywords
- Better conversion rates
Use this data to double down on what’s working and fix what isn’t.
Modern & Advanced SEO Techniques in 2025
AI and Machine Learning in SEO
Search engines now use AI to understand intent better. Write naturally and focus on solving real problems.
Voice Search Optimization
Optimize for questions like “How do I clean a leather sofa?” Use FAQs and conversational content.
Visual and Video Search Optimization
Use high-quality images with proper alt text. For videos, optimize titles, thumbnails, and descriptions.
Core Web Vitals and Page Experience
This includes:
- Loading speed
- Interactivity
- Visual stability Google rewards websites with better user experiences.
Final Thoughts
SEO is not a shortcut—it’s a smart strategy. It helps you build a strong foundation, connect with your audience, and grow your business sustainably.
Just like planting a tree, it takes time, but once it grows, it provides value for years.

Passionate about blogging and focused on elevating brand visibility through strategic SEO and digital marketing. Always tuned in to the latest trends, I’m dedicated to maximizing engagement and delivering measurable ROI in the dynamic world of digital marketing. Let’s connect and unlock new opportunities together!

