Summary
Porsche, a renowned German luxury car manufacturer, is known for its high-performance sports cars and engineering excellence. This SWOT analysis examines the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in 2025. The analysis highlights Porsche’s strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, innovative capabilities, and the impact of the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and software-driven technologies. Insights from this analysis can guide strategies for maintaining Porsche’s competitive advantage in the luxury automotive industry.
SWOT Analysis of Porsche
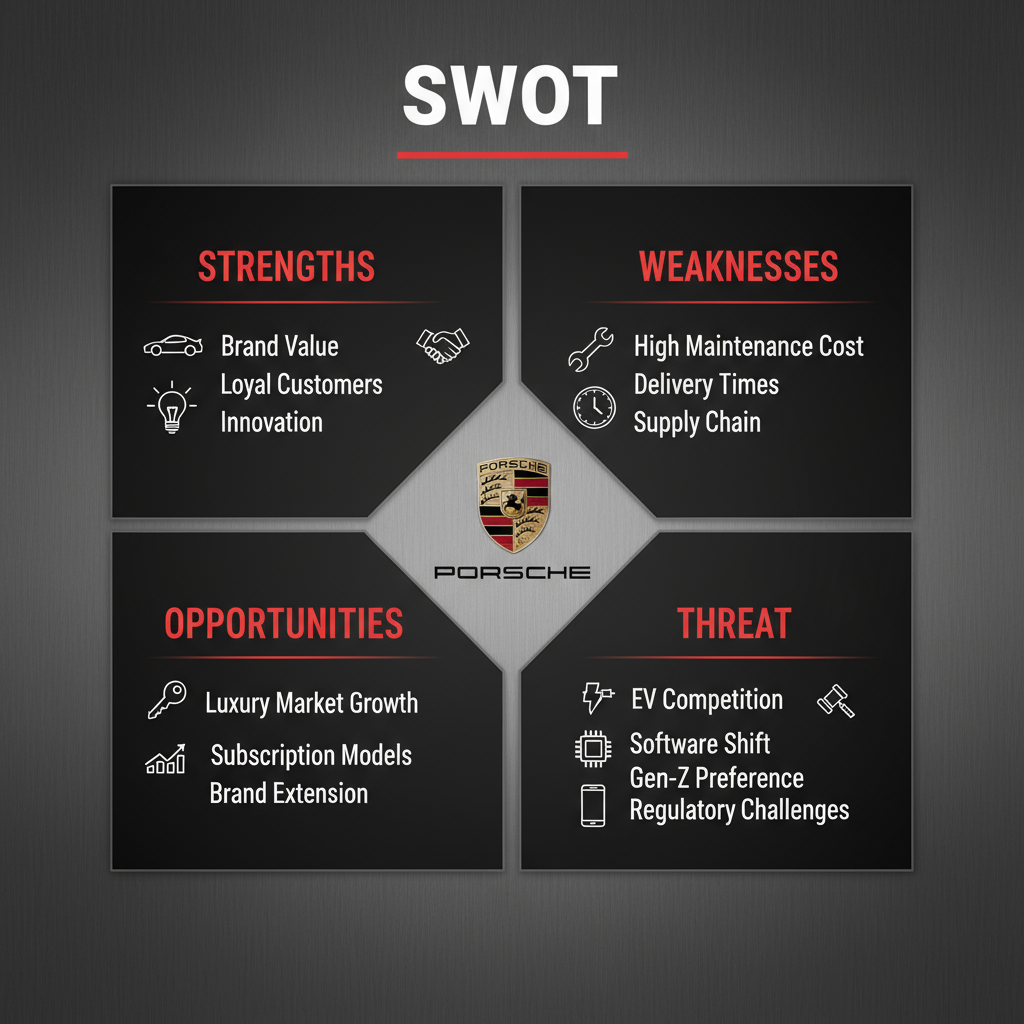
A SWOT analysis identifies the internal and external factors influencing Porsche’s business. Strengths and weaknesses are internal aspects, while opportunities and threats come from external market conditions and industry trends.
Porsche Strengths

Porsche’s strengths are the foundation of its global success. They reflect its heritage, engineering excellence, and strong market positioning.
1. Brand value and reputation
Porsche is one of the most valuable luxury car brands in the world. Its estimated brand value reaches $33.7 billion, placing it at the top of global luxury rankings. Customers perceive Porsche as a symbol of quality, prestige, and high performance. This reputation allows the company to maintain strong sales despite a niche market.
2. Loyal customer base
Porsche has a dedicated customer base. Long-term sales data show consistent growth with a 7.6% CAGR. The company attracts high-net-worth individuals, celebrities, and car enthusiasts. High brand loyalty, measured at 57.4% by J.D. Power, ensures repeat purchases and sustained demand.
3. Ability to sell cars with high margins
Porsche achieves high profitability compared to other Volkswagen Group brands. In 2022, it generated 29% of the group’s profits while selling significantly fewer units than mass-market brands. High operating margins of over 18% demonstrate efficiency and strong financial performance.
4. Culture of innovation and excellence
Porsche continuously introduces advanced automotive technologies. Examples include vehicle-to-X communication for autonomous driving, high-voltage battery systems for EVs, and advanced LED lighting. Its venture capital arm, Porsche Ventures, invests in innovative startups to leverage new technologies for performance and sustainability.
5. Driver experience and motorsport heritage
Porsche cars provide a unique driving experience, blending precision handling, acceleration, and performance. Motorsport heritage, including 19 Le Mans wins, strengthens the emotional connection with customers. This heritage translates into exceptional road car dynamics.
6. Synergic advantages of being part of Volkswagen Group
Porsche benefits from shared R&D, manufacturing, and supplier networks within Volkswagen. Collaborations on electric and hybrid technology enhance its EV development. Access to a global distribution network improves market reach without diluting brand identity.
7. Messaging luxury through strategic collaborations
Porsche enhances its luxury image through collaborations with brands like TAG Heuer and Embraer. Limited-edition products and lifestyle partnerships reinforce Porsche’s brand beyond automobiles, creating new revenue streams and brand prestige.
Porsche Weaknesses

Porsche faces internal challenges that may affect customer satisfaction, operations, and growth.
1. High maintenance cost
Porsche vehicles are expensive to maintain. Over ten years, maintenance costs can reach $22,075, higher than many luxury competitors. Repair probability above $500 by year 10 is 51.17%, making ownership costly for consumers.
2. Higher delivery time
Delivery times for certain Porsche models, particularly the Taycan EV, range from six to twelve months. Long wait periods may discourage potential buyers and give competitors an advantage.
Also Read: SWOT Analysis of Lamborghini
3. Supply chain vulnerabilities
Porsche is sensitive to supply chain disruptions. Shortages of semiconductors, material price increases, and geopolitical events like Russia’s invasion of Ukraine have halted production temporarily. Dependency on single-source suppliers, such as Ukrainian wire harnesses for the Taycan, exposes operational risks.
Porsche Opportunities

External factors present opportunities for Porsche to expand its business, revenue, and market share.
1. Luxury car market poised for faster, profitable growth
The luxury automotive segment is growing faster than mass-market vehicles, with annual growth between 8 to 14%. Porsche’s price range of $80,000 to $300,000 positions it to benefit from high-margin sales in this expanding market.
2. Luxury cars are going global
Emerging markets, particularly China, are driving growth in luxury car sales. Porsche delivered 93,286 units in China in 2022, representing 30% of global sales. The expanding ultra-high-net-worth population in Asia provides significant opportunities for market expansion.
3. Growth in subscription-based model
Porsche Drive subscription services allow customers to access vehicles for flat fees covering insurance, maintenance, and taxes. This model appeals to younger consumers and promotes brand engagement while creating new revenue streams.
4. Vertical brand extension opportunities
Porsche can leverage its brand value to enter luxury lifestyle markets. Already offering e-bikes, apparel, and model cars, Porsche can extend into watches, yachts, private jets, or high-end furniture. These extensions strengthen brand recognition and diversify revenue.
Porsche Threats

Porsche faces several external threats that may impact its market position and future profitability.
1. Everything about car making will change with EVs
The transition to EVs is reshaping automotive engineering. New tech-centric players, particularly in China and the US, are challenging traditional carmakers. Electric motors simplify vehicle design, reducing barriers to entry and enabling competitors to match or exceed Porsche’s performance.
2. Value shift from hardware to software
Software is becoming a critical differentiator in cars. Advanced driver-assistance systems, over-the-air updates, battery management, and charging solutions now drive customer preferences. Porsche must invest heavily in software development to remain competitive.
3. Gen-Z’s declining interest in car ownership
Younger generations prioritize ridesharing, ecological concerns, and convenience over car ownership. This shift in mindset may reduce the demand for high-end vehicles in the long term, requiring Porsche to adapt marketing and product strategies.
4. Regulatory challenges in the auto industry
Stringent regulations for emissions, battery recycling, and autonomous driving increase operational costs and complexity. Porsche aims to increase EV share to over 80% by 2030 and achieve CO2-neutral production. Compliance and sustainability initiatives are essential to mitigate regulatory risks.
Conclusion
Porsche has a strong brand, loyal customers, and high-margin products supported by innovation and motorsport heritage. Opportunities in global luxury markets, subscriptions, and brand extensions offer growth potential. However, threats from EVs, software shifts, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures require strategic adaptation. Porsche’s ability to innovate in technology and maintain brand prestige will determine its success in the evolving automotive landscape.
FAQs
What is Porsche’s current market position?
Porsche is a leading luxury car manufacturer, known for performance, innovation, and a strong global presence.
How does Porsche maintain brand loyalty?
Through superior driving experiences, motorsport heritage, and a focus on customer satisfaction and exclusivity.
What are Porsche’s main weaknesses?
High maintenance costs, longer delivery times, and supply chain vulnerabilities are key internal weaknesses.
How is Porsche adapting to EVs?
Porsche is investing in electric vehicle technologies, expanding the Taycan lineup, and leveraging Volkswagen Group resources for R&D.
What external threats does Porsche face?
EV competition, software-driven differentiation, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory challenges are major threats.
Can Porsche expand into non-automotive markets?
Yes, Porsche has opportunities for vertical brand extension, including luxury lifestyle products like watches, yachts, and furniture.
How important is Porsche’s motorsport heritage?
Motorsport heritage strengthens brand image, enhances driving experience, and builds emotional connections with customers.
A digital marketer with a strong focus on SEO, content creation, and AI tools. Creates helpful, easy-to-understand content that connects with readers and ranks well on search engines. Loves using smart tools to save time, improve content quality, and grow online reach.

