The internet connects people across the globe, and your business has the power to reach audiences far beyond your local market. But simply having a website isn’t enough—you need to optimize it for different languages, cultures, and search engines. That’s where International SEO comes in.
International SEO is the process of optimizing your website so search engines can easily identify which countries and languages you are targeting. Whether you’re running an eCommerce store, SaaS platform, or content publication, international SEO helps you attract global traffic and grow your brand worldwide.
Key Differences Between International SEO and Local SEO
While local SEO focuses on reaching people in a specific area or city, international SEO is about making your site visible to users across different countries and languages. Here are some key differences:
- Audience: Local SEO targets nearby users, while international SEO targets global visitors.
- Domain Structure: International SEO often uses country-code domains (like .fr, .de) or subfolders (/fr/, /de/) to serve content to specific regions.
- Content Strategy: International SEO requires translation, localization, and cultural adaptation of content, whereas local SEO focuses on regional relevance.
How Search Engines Handle International Content
Search engines like Google want to serve users the most relevant content, in their language and for their location. Here’s how they do it:
- Hreflang Tags: These tags tell search engines which version of your page to serve based on language and region.
- Geotargeting: Search engines look at domain structures, server location, and Google Search Console settings to determine your target country.
- Language Detection: Algorithms scan your website to identify the language of the content.
Correctly using these signals helps search engines show the right version of your site to the right users.
Choosing the Right International SEO Strategy
Your international SEO approach depends on whether you’re targeting users by country or language.

a. Targeting by Country
You create different versions of your site for each country (e.g., one for the UK, one for Canada). Use:
- ccTLDs like example.fr, example.de
- Subdirectories like example.com/fr/, example.com/de/
- Subdomains like fr.example.com, de.example.com
b. Targeting by Language
You serve the same version to all users speaking a particular language.
Each strategy has pros and cons. For example, ccTLDs are great for local trust, but cost more and require separate SEO efforts. Subdirectories are easier to manage, but may not be as geo-specific.
Best Practices for International SEO
a. Use hreflang Tags Correctly
These tags tell search engines what language and region a page is for. For example:
Tip: Always pair hreflang with a self-referencing tag and include it in your sitemap.
b. Select the Right URL Structure
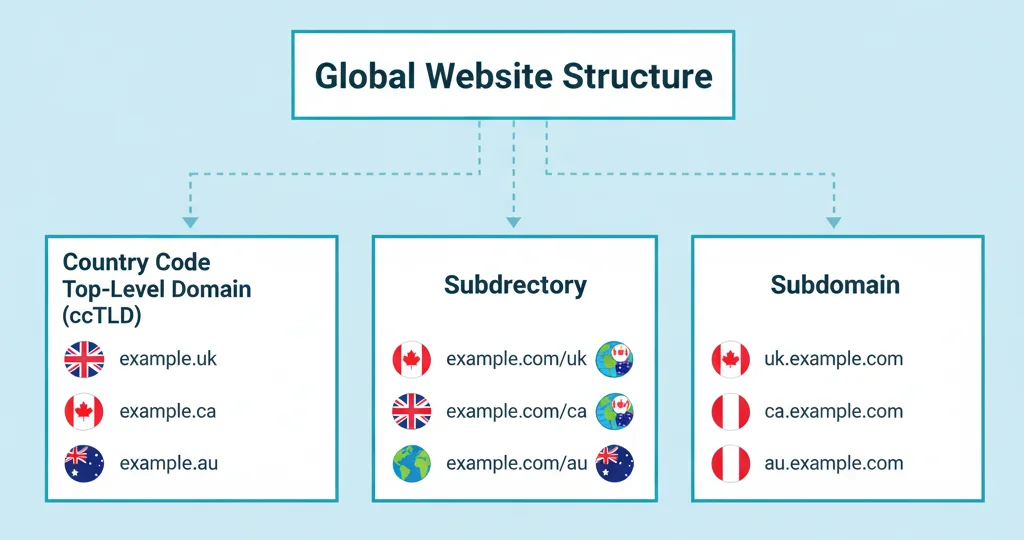
Each URL structure has its advantages:
- ccTLDs: Great for trust but harder to manage.
- Subdomains: Easy to separate content but harder for SEO.
- Subdirectories: Best for centralized management and authority.
Choose what aligns with your business size and SEO goals.
c. Localize Content, Don’t Just Translate
A simple translation won’t work. Localization involves adapting:
- Currency and date formats
- Idioms and cultural references
- Product offerings and local laws
d. Optimize for Local Keywords
Don’t assume the same keywords apply across borders. Use tools like:
- Google Keyword Planner (set to target location)
- SEMrush and Ahrefs (country-based filters)
Direct translations often miss local search intent, so local keyword research is a must.
e. Use Local Hosting or a CDN
Page speed matters for SEO. Host your site near your users or use a CDN like Cloudflare or Akamai to ensure fast global performance.
f. Adapt to Regional Search Engines
Google isn’t the only player. Depending on your target region:
- Baidu for China
- Yandex for Russia
- Naver for South Korea
Each has different ranking factors, so tailor your SEO accordingly.
g. Create Multilingual Sitemaps
Multilingual XML sitemaps make it easier for search engines to understand your site’s structure. Include hreflang annotations and submit to Google Search Console.
h. Set Up Google Search Console for Multiple Countries
Create properties for each domain or subfolder, and set geographic targets using the International Targeting report in Google Search Console.
Technical SEO Considerations for Global Sites

Going global introduces technical challenges:
- Mobile-First Indexing: Ensure your international sites are mobile-friendly across all devices.
- Canonical Tags: Avoid duplicate content issues by setting canonical URLs correctly, especially when similar content exists in different languages.
- Crawl Budget: Large international websites can overwhelm crawlers. Optimize site structure, limit duplicate pages, and submit updated sitemaps.
Measuring International SEO Performance
Track the success of your efforts with clear metrics:
- International traffic growth (via Google Analytics)
- Keyword rankings in different countries
- Bounce rates and engagement by region
- Conversion rates by country or language
Use tools like:
- Google Search Console (International Targeting, Performance reports)
- SEMrush or Ahrefs (Geo-targeted keyword tracking)
- Screaming Frog (Hreflang validation and audit)
Common International SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Not using hreflang or using it incorrectly
- Automatically translating content with no localization
- Using same keywords and content for all markets
- Not considering cultural and legal differences
- Forgetting to set geographic targets in Google Search Console
Avoiding these errors can save you from major traffic drops and indexing problems.
Tools to Help with International SEO
Here are some reliable tools to streamline your global SEO:
| Tool | Purpose |
| Google Search Console | Geo-targeting and performance tracking |
| SEMrush / Ahrefs | Country-specific keyword and backlink analysis |
| Screaming Frog | Technical SEO and hreflang audits |
| Weglot / Smartling | Website localization and translation management |
| Cloudflare / Akamai | CDN for fast global delivery |
Conclusion
International SEO opens the doors to a global audience, but it takes more than just translating your content. By following the best practices—like using proper hreflang tags, localizing your content, selecting the right domain structure, and optimizing for regional search behavior—you can create a successful international presence that drives real growth.
Start small, test your strategy, and expand as you learn what works in each region.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between international SEO and multilingual SEO?
International SEO focuses on targeting users in different countries and languages. Multilingual SEO only focuses on different languages, not necessarily different regions.
2. How do I implement hreflang tags correctly?
Use hreflang tags in the head section of each page or in your sitemap. Always include self-referencing tags and match languages and regions accurately.
3. Can I rank in different countries with the same domain?
Yes. You can use subdirectories or subdomains for each region and set up proper hreflang and geotargeting signals.
4. Do I need separate websites for each country?
Not necessarily. You can manage international SEO through subfolders or subdomains. Separate websites may be needed for complex localization needs.
5. How long does it take to see results from international SEO?
It can take a few months to see significant results, depending on your strategy, competition, and market size. Be patient and monitor performance consistently.

Passionate about blogging and focused on elevating brand visibility through strategic SEO and digital marketing. Always tuned in to the latest trends, I’m dedicated to maximizing engagement and delivering measurable ROI in the dynamic world of digital marketing. Let’s connect and unlock new opportunities together!

